Shortening distances: providing healthcare to indigenous communities in Venezuela’s Delta Amacuro state
20 July 2023
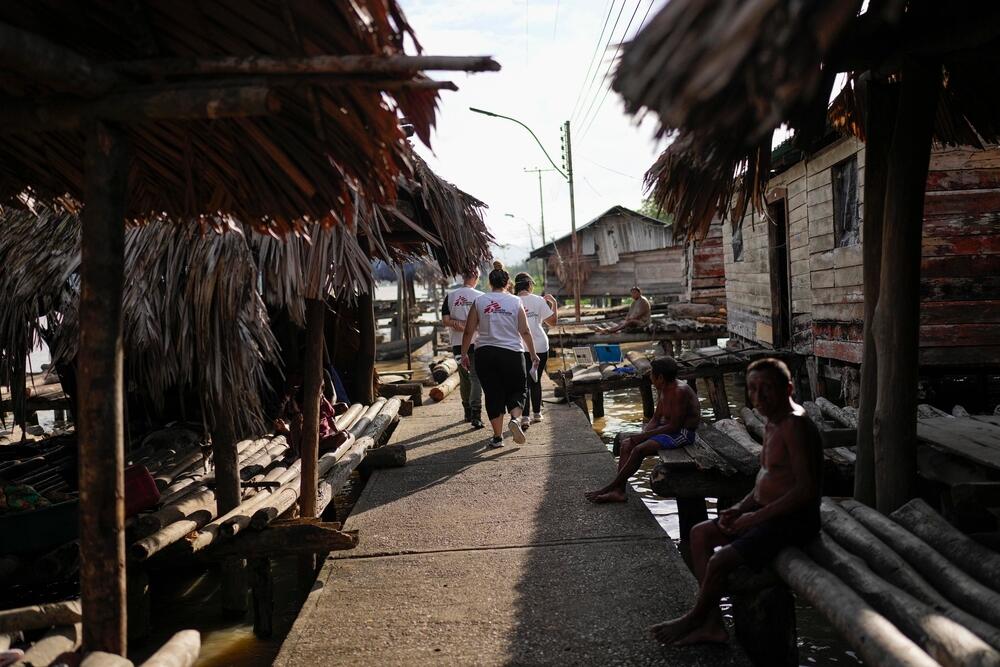
Rivers serve as roads and tropical rainforest stretches to the horizon in Delta Amacuro state, a vast area bordering the Atlantic Ocean in northeastern Venezuela. Largely inaccessible, this region is home to a large number of Indigenous communities who face significant challenges accessing healthcare.
Eighteen-year-old Adelia is 38 weeks pregnant but has had no antenatal check-ups. A member of the Warao indigenous community, as soon as her labour pains started, she planned to visit the wisirato, a spiritual healer and purveyor of traditional medicine who plays a significant role in her culture. But when the labour pains began, they were so strong that Adelia felt afraid.
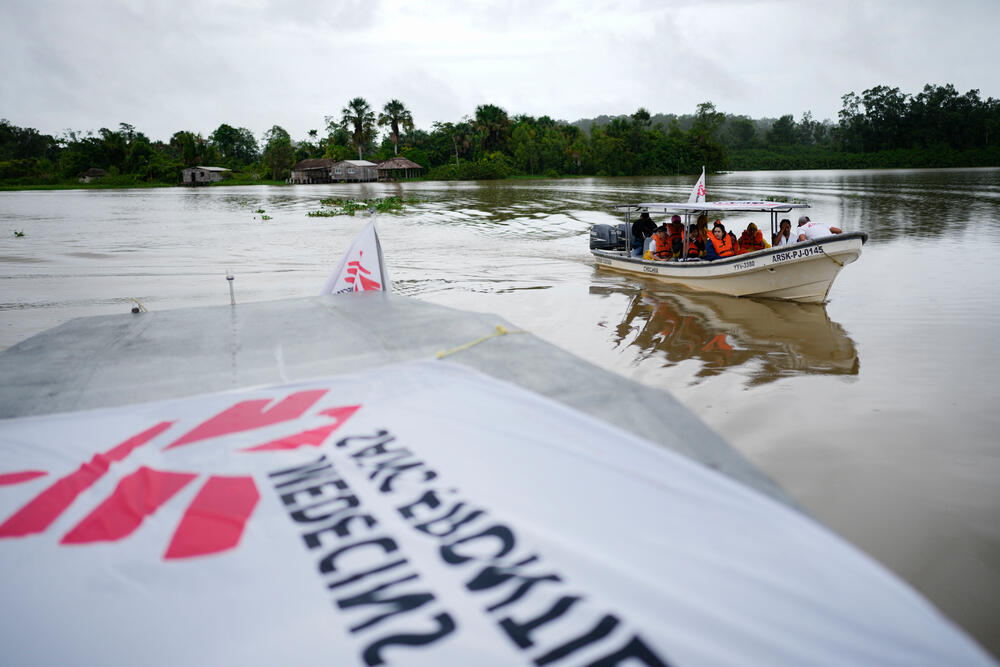
One day earlier, Adelia had noticed two boats bearing flags with a red figure on a white background sailing down the Orinoco River. She recognised them as belonging to international medical organisation Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders (MSF) and realised they were on their way to the nearby community of Nabasanuka to provide medical care.
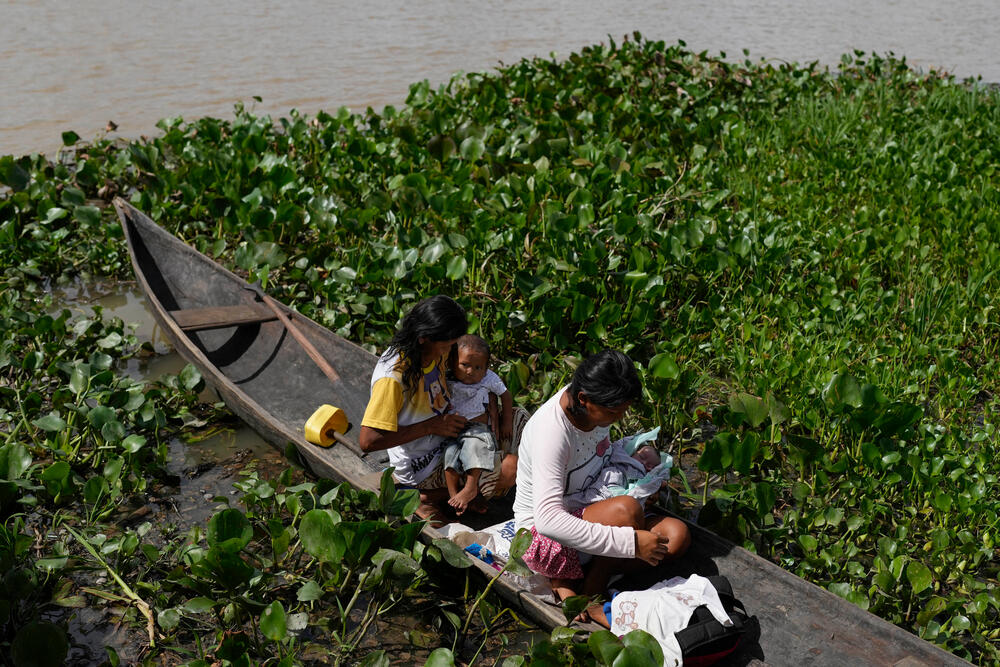
Having persuaded her mother to accompany her to the outpatient clinic in Nabasanuka, they set off to paddle the two-hour journey on a long, lightweight wooden boat called a curiara.
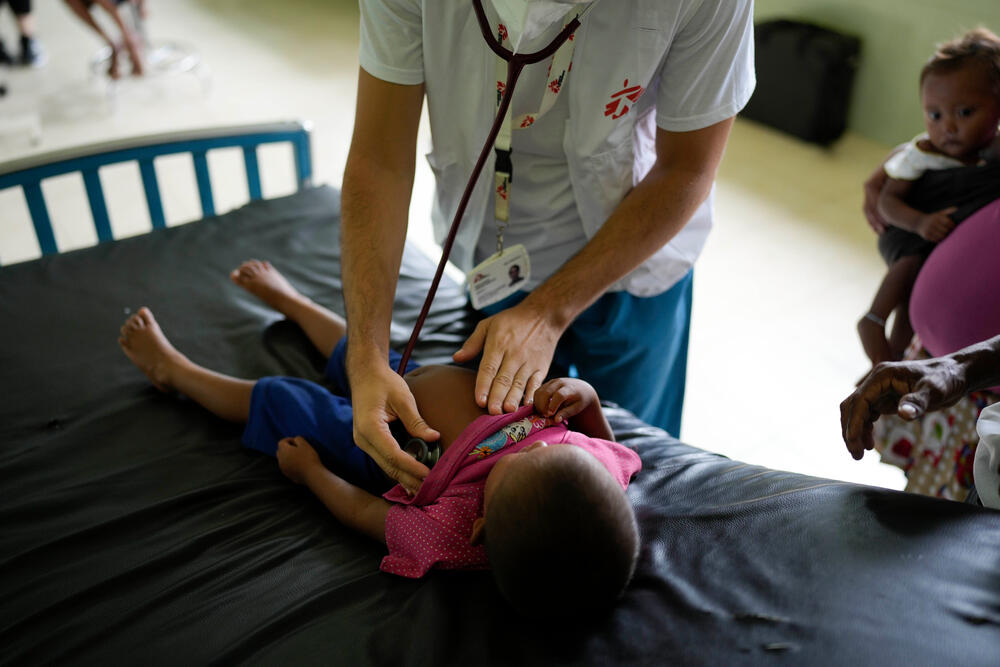
In the delivery room at Nabasanuka clinic, Adelia feels almost overwhelmed by the heat and humidity. But, on the instructions of the medical team, she pushes hard and with determination. Because of her young age and the lack of medical oversight during the pregnancy, Adelia's birth was viewed by health staff as high risk. But despite this, and the limitations of a health centre with only basic facilities, at 9.30 in the morning, Adelia hears for the first time the cry of her son José Antonio, a strong and healthy baby who measures 52 cm.
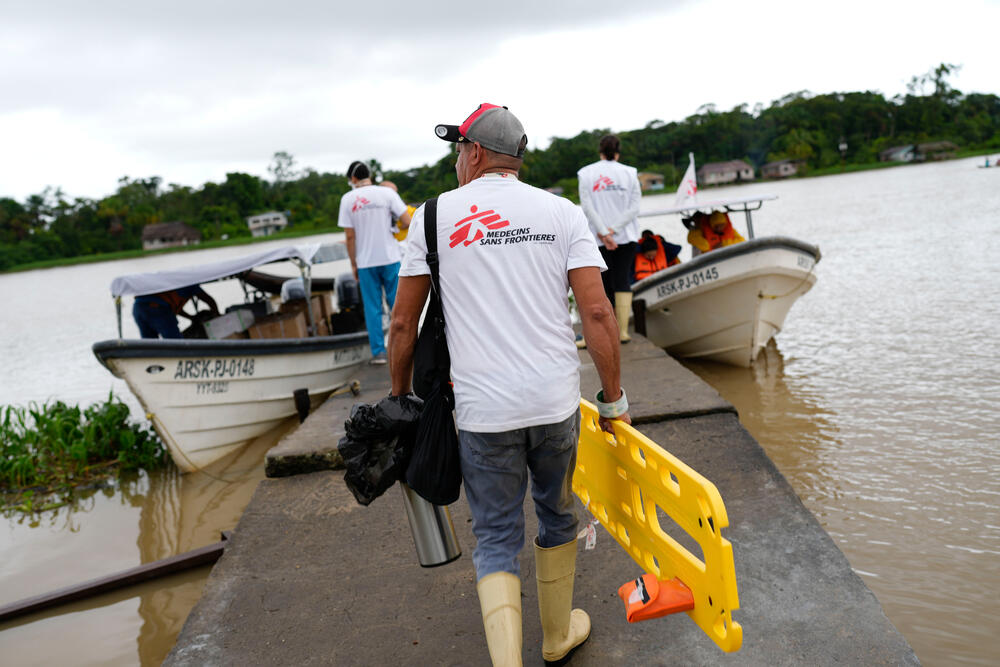
Since July 2022, MSF teams have been working alongside local authorities to bring basic healthcare to isolated communities across Delta Amacuro state. Access is a challenge in itself: the state encompasses more than 40,000 square km and is heavily forested. Most indigenous communities live scattered along the banks of the Orinoco River, which is the region’s main highway. To reach the clinics where they provide medical care, MSF teams must travel by motorboat for at least six hours from the state capital, Tucupita, while patients often have to paddle their canoes for hours or even days to see a doctor.
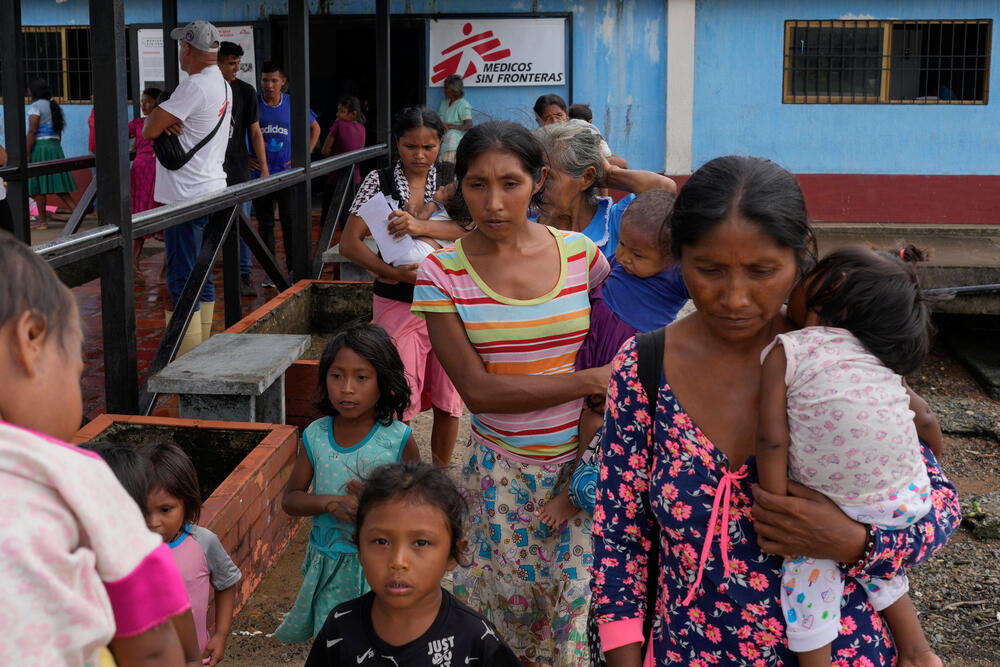
The Indigenous communities in this region suffer from a range of preventable diseases caused by the precarious conditions in which they live and the multiple barriers they face accessing healthcare. These include waterborne diseases such as parasitosis and diarrhoea; diseases spread by mosquitoes and other insects, such as malaria; respiratory infections; skin conditions; and malnutrition. An absence of antenatal and postnatal care increases the risks for pregnant women and their babies.
Local people’s difficulties accessing health services are aggravated by language barriers and cultural differences with visiting medical teams, as well as shortages of drugs and medical supplies across the region. "Difficulties in staffing these remote locations and the lack of supplies and medicines also contribute to people’s challenges in obtaining adequate and quality medical care," says Carlos Dominguez, MSF project coordinator in Delta Amacuro.
"Difficulties in staffing these remote locations and the lack of supplies and medicines also contribute to people's challenges in obtaining adequate and quality medical care."
Working with local authorities, MSF works in two outpatient clinics in the communities of San Francisco de Guayo and Nabasanuka, both in Antonio Díaz municipality in the east of the state. For three weeks in every month, a multidisciplinary MSF team – made up of doctors, nurses, pharmacists, water and sanitation specialists, logisticians and health promoters – base themselves at the health point, providing general medical care to around 70 patients a day.
Health promotion is an important aspect of MSF's work in Delta Amacuro. "By providing people with information, it is possible to raise awareness about healthy practices, proper hygiene and disease prevention, without neglecting the community's own traditions," says Dominguez. “Not only does this have a direct impact on people's health, but it also fosters community empowerment and a proactive approach to health.”
MSF also arranges hospital transfers for patients who need specialist care. This morning, MSF’s medical team contacted health authorities to request an ambulance-boat from Tucupita for three-year-old Jesus, who needs urgent treatment that is unavailable in Nabanasuka. Jesus’ parents paddled their canoe for four hours to bring him to Nabanasuka clinic; it would take them seven days to paddle on to Tucupita, compared to a journey by ambulance of six hours.
MSF’s work in Delta Amacuro state is testament to the importance of providing basic medical services to everyone, regardless of their geographic location or circumstances, and to MSF’s belief that healthcare is a fundamental right of every individual, which must be fulfilled in even the most remote and disadvantaged regions.
"When a doctor is next to a village, the people feel calm and happy."
At Nabansuka clinic, Adelia is talking with an MSF health promoter about the benefits of breastfeeding. "Yakera wito," she says, with a big smile. This means ‘hello’ in the Warao language but is also a way of expressing gratitude.
The scene is witnessed by a Warao community leader, who observes: "When a doctor is next to a village, the people feel calm and happy."
Adelia is now ready to make her way upriver and back home to introduce baby José Antonio to the rest of his community.
MSF has been working in Venezuela since 2015. Currently its teams work in the states of Amazonas, Anzoátegui, Bolívar and Delta Amacuro alongside national authorities, with the aim of strengthening the public health system and providing medical care to vulnerable people.